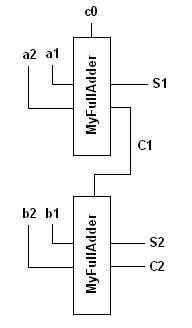
The aim of this example is it to be able to build a 2-bit full-adder using two 1-bit full-adder modules as shown below.

The 1-bit full-adder module should be built using logic gates. The code is as follows.
#include <lcs/or.h> #include <lcs/and.h> #include <lcs/not.h> #include <lcs/tester.h> // All classes of the libLCS are defined in the namespace lcs. using namespace lcs; // Define a class MyFullAdder. This is our 1-bit full-adder module. class MyFullAdder { public: // The constructor should take single line Bus<1> objects as inputs, one each for // the two data lines, carry input, sum output and the carry output. MyFullAdder(const Bus<1> &S, const Bus<1> &Cout, const Bus<1> &A, Bus<1> &B, Bus<1> &Cin); // The destructor. ~MyFullAdder(); private: // a, b, c are the two data inputs and the carry input respectively. Bus<1> a, b, c; // s is the sum output, and cout is the carry output. Bus<1> s, cout; // A pointer member for each of the gates which constitute our FullAdder. // The number and type of the gates is same as in the 1st basic example. Not *n1, *n2, *n3; And<3> *sa1, *sa2, *sa3, *sa4; And<3> *ca1, *ca2, *ca3, *ca4; Or<4> *so, *co; }; MyFullAdder::MyFullAdder(const Bus<1> &S, const Bus<1> &Cout, const Bus<1> &A, Bus<1> &B, Bus<1> &Cin) : a(A), b(B), c(Cin), s(S), cout(Cout) { Bus<> a_, b_, c_, s1, s2, s3, s4, c1, c2, c3, c4; // Each of the gates should be initialised with proper bus connections. // The connections are same as in the 1st basic example. n1 = new Not(a_, a); n2 = new Not(b_, b); n3 = new Not(c_, c); // Initialising the NOT gates. sa1 = new And<3>(s1, a_*b_*c); sa3 = new And<3>(s3, a*b_*c_); // Initialising the AND gates for the sa2 = new And<3>(s2, a_*b*c_); sa4 = new And<3>(s4, a*b*c); // minterms corresponding to the sum output. ca1 = new And<3>(c1, a_*b*c); ca2 = new And<3>(c2, a*b_*c); // Initialising the AND gates for the ca3 = new And<3>(c3, a*b*c_); ca4 = new And<3>(c4, a*b*c); // minterms corresponding to the sum output. so = new Or<4>(s, s1*s2*s3*s4), co = new Or<4>(cout, c1*c2*c3*c4); // Initialising the OR gates which // generate the final outputs. } MyFullAdder::~MyFullAdder() { // The destructor should delete each of the gates // which were initialised during construction. delete n1; delete n2; delete n3; delete sa1; delete sa2; delete sa3; delete sa4; delete ca1; delete ca2; delete ca3; delete ca4; delete so; delete co; } int main(void) { Bus<> a1, b1, a2, b2, c0(0), S1, C1, S2, C2; // Note that the bus c0 (the carry input to the first full-adder) // has been initialised with a value of 0 (or lcs::LOW) on its line. // Initialising the 1-bit full adder modules. MyFullAdder fa1(S1, C1, a1, a2, c0), fa2(S2, C2, b1, b2, C1); Tester<4, 3> tester(a1*b1*a2*b2, S1*S2*C2); tester.run(); return 0; }
Back to all examples.
 1.4.7
1.4.7